Cemented Carbide - All about this material
What is cemented carbide?
Cemented carbide (also known as solid carbide or tungsten carbide (WC)) is one of the most successful composite engineering materials ever produced. Its unique combination of strength, hardness, and toughness satisfies the most demanding applications.
A key feature of the cemented carbide is the potential to vary its composition so that the resulting physical and chemical properties ensure maximum resistance to wear, deformation, fracture, corrosion, and oxidation. In addition, the wide variety of shapes and sizes that can be produced using modern powder metallurgical processing offers tremendous scope to design cost-effective solutions to many of the problems of component wear and failure encountered in both the engineering and domestic environment.
Engineering materials
The most commonly used materials are shown schematically relative to their hardness and toughness properties: diamond (PCD) is the hardest of all, followed by cubic boron nitride (CBN), and ceramics (Al2O3, SiC, SIALON, etc.). The super-hard materials all suffer from lower toughness and poor resistance to sudden fracture, the cemented carbides have a unique combination of high hardness and good toughness within a wide range and thus constitute the most versatile hard materials group for engineering and tooling applications.
What is the most valuable property of Cemented Carbide?
The most valuable property of cemented carbide is that it offers a solution safer and more dependable than that of any other known material to one of the toughest problems that engineers have to contend with – reliability.
Reliability is often a problem of wear. Wear resistance is the most outstanding feature of cemented carbide. Cemented carbide can also withstand deformation, impact, heavy load, high pressure, corrosion, and high temperature – often the only material that can fulfill these requirements satisfactorily.
It has long been a well-known fact that the use of cemented carbide provides an optimal solution in the case of tools for metal cutting and rock drilling. Over the years, cemented carbides have also proven their superiority in a great number of other tooling and engineering applications.
Hyperion Materials & Technologies developments on Cemented Carbide
From raw material to your needs, Hyperion Materials & Technologies develops cemented carbide technology to meet our present and future customers’ needs. From atomic engineering of crystal grain boundaries to the customer-specific design of a rotary cutting station, Hyperion’s research and development is dedicated to advancing the frontiers of cemented carbide technology. Every stage in the manufacture of a cemented carbide component – from powder production to finishing – is crucial to ensuring optimum performance. At Hyperion, we take pride in having full control of each processing step and in developing proprietary production processes that further improve our technological capabilities.
Our mission is to develop new products and new grades of cemented carbide that enhance our customers’ operations through superior performance and reduced costs.
Which are the most relevant attributes related to cemented carbide?
Electrical and magnetic properties
Which are the types and sizes for cemented carbide?
The cemented carbides are a range of composite materials that consist of hard carbide particles bonded together by a metallic binder.
The carbide phase is generally between 70 and 97% of the total weight of the composite. Its grain size averages between 0.4 and 10 μm.
Tungsten carbide (WC), the hard phase, together with cobalt (Co), the binder phase, forms the basic cemented carbide structure from which other types of cemented carbide have been developed. In addition to the straight tungsten carbide – cobalt compositions – cemented carbide may contain varying proportions of titanium carbide (TiC), tantalum carbide (TaC), and niobium carbide (NbC). These carbides are mutually soluble and can also dissolve a high proportion of tungsten carbide. Also, cemented carbides are produced that have the cobalt binder phase alloyed with, or completely replaced by, other metals such as iron (Fe), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), molybdenum (Mo), or alloys of these elements.
There are three individual phases that make up cemented carbide. In metallurgical terms, the tungsten carbide phase (WC) is referred to as the a-phase (alpha), the binder phase (i.e., Co, Ni etc.) as the b-phase (beta), and any other single or combination of carbide phases (TiC, Ta/NbC, etc.) as the g-phase (gamma). Other than for metal cutting applications, there is no internationally accepted classification of cemented carbides.
Types and sizes:
How is cemented carbide made?
Hyperion Materials & Technologies’ cemented carbide manufacturing process begins with the composition of a specific tungsten carbide powder mixture – tailored for the application.
The tungsten carbide powder is compacted into a form.
In a high-temperature sintering furnace, the tungsten carbide structure of the blank is shaped at precise temperatures for strictly defined periods. During this heat treatment, the tungsten carbide blank undergoes shrinkage of some 50% in volume.
The sintered cemented carbide component gains its final finish by additional grinding, lapping, and/or polishing processes.
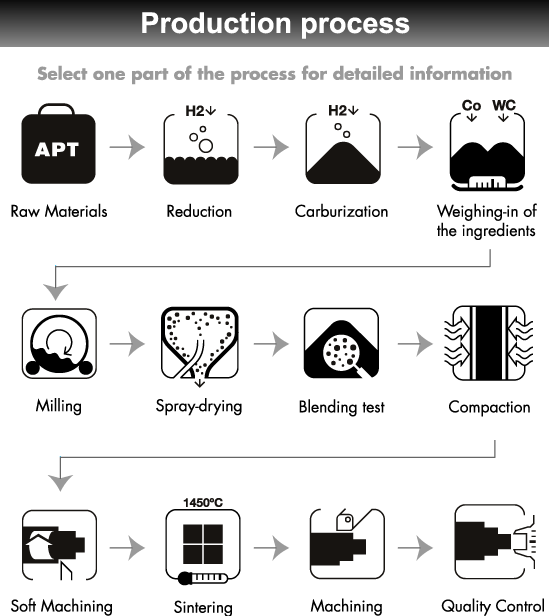
Hyperion is continuously developing new cemented carbides. In 2017, Hyperion established a new Carbide Research & Development Center, located in the Can Tooling Competence Center in Barcelona. The R&D Center employs researchers focused on developing next generation materials, products, and process technologies. Innovations in cemented carbide include addition of unique materials to affect grain size to unique materials to affect hardness to development of Hyperion's unique sinter-HIP process.
Visit our Products pages for additional information about our cemented carbide solutions:
Toolmaker Solutions
Engineered Solutions
Hyperion Materials & Technologies is a leading manufacturer of cemented carbide solutions featured in applications and services within the areas of can making, aerospace, automotive, pump and seal, oil and gas, metal forming, metalworking, and hygiene products.
Your Hyperion salesperson can offer their expertise in selecting the cemented carbide product best suited to solve your needs.